Research Area: Artificial Intelligence (AI)
-
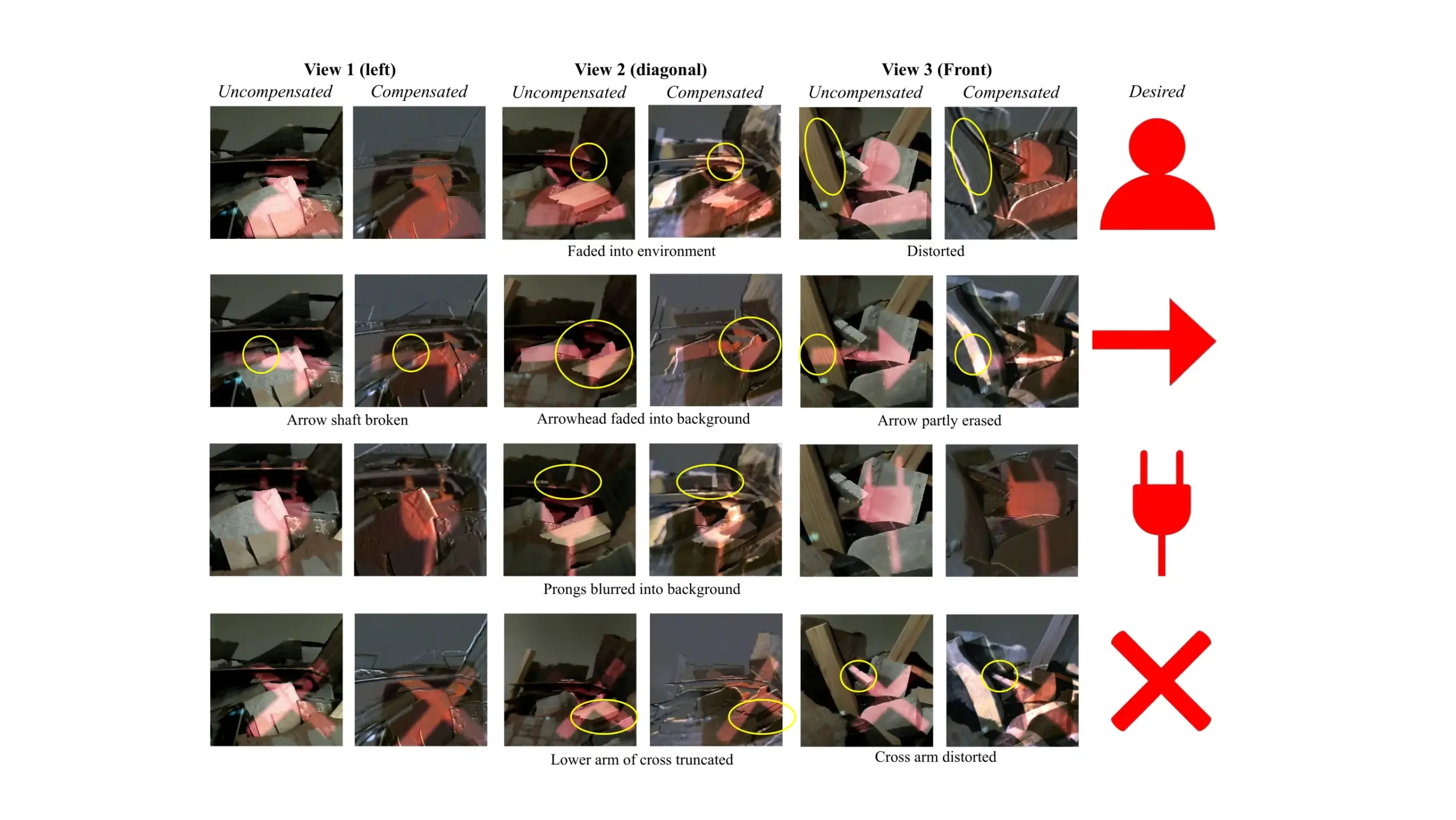

Evaluating Dynamic Surface Compensation for Robots with Projected AR
Abstract Projector-based augmented reality (AR) enables robots to communicate spatially-situated information to multiple observers without requiring head-mounted displays, e.g., projecting navigation path. However, they require flat and weakly textured projection surfaces; otherwise, the surface needs to be compensated to retain the original projected image. Yet, existing compensation methods assume static projector-camera-surface configurations and may not…
-
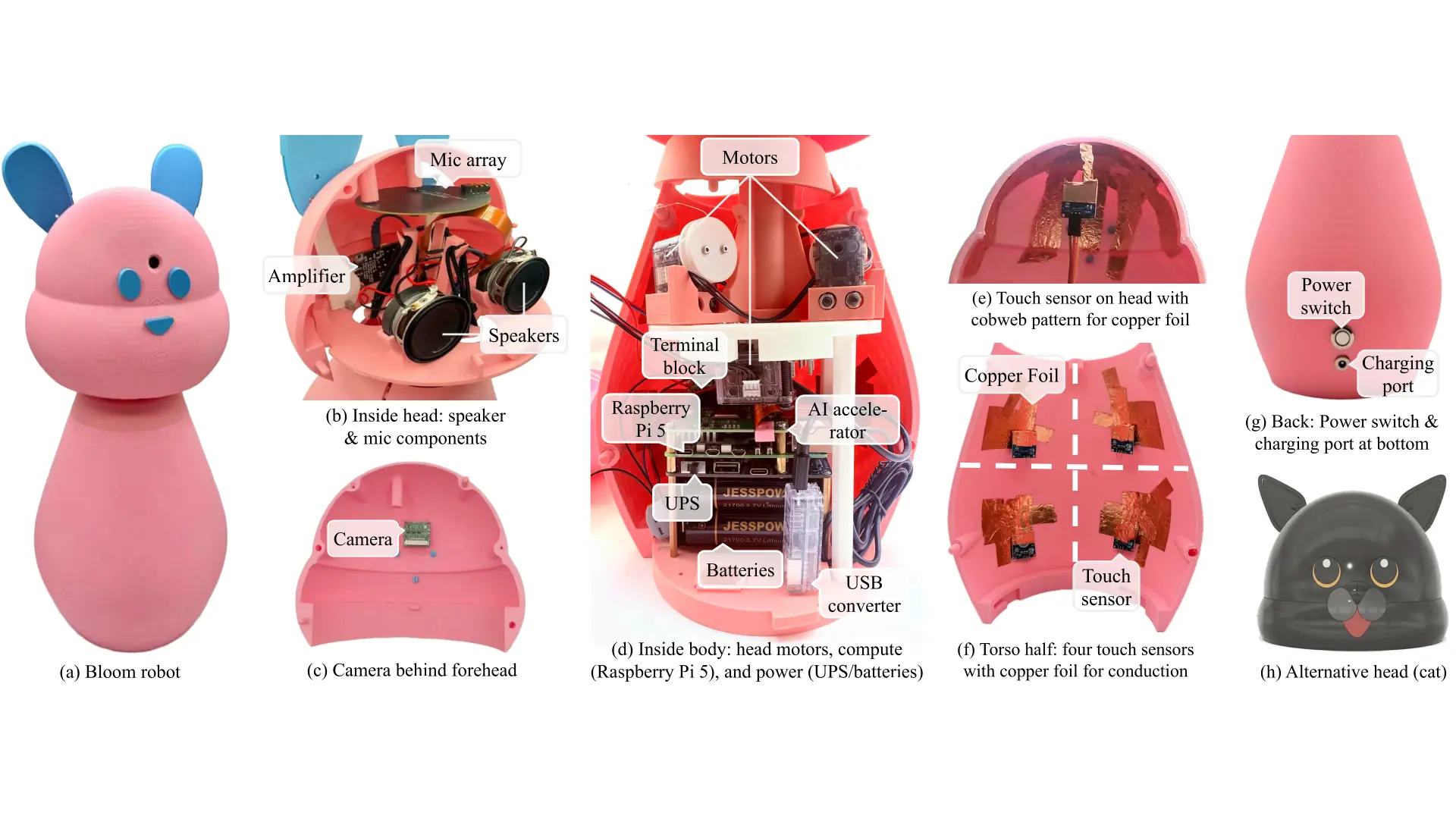
Bloom Preview: A Low-Cost LLM-Powered Social Robot
Abstract HRI research shows that social robots support human companionship and emotional well-being. However, the cost of high-end social robots limits their accessibility, and, yet, existing low-cost platforms cannot fully support users emotionally due to limited interaction capabilities. In this demo paper with accompanying video, we showcase Bloom, a low-cost social robot that combines touch…
-
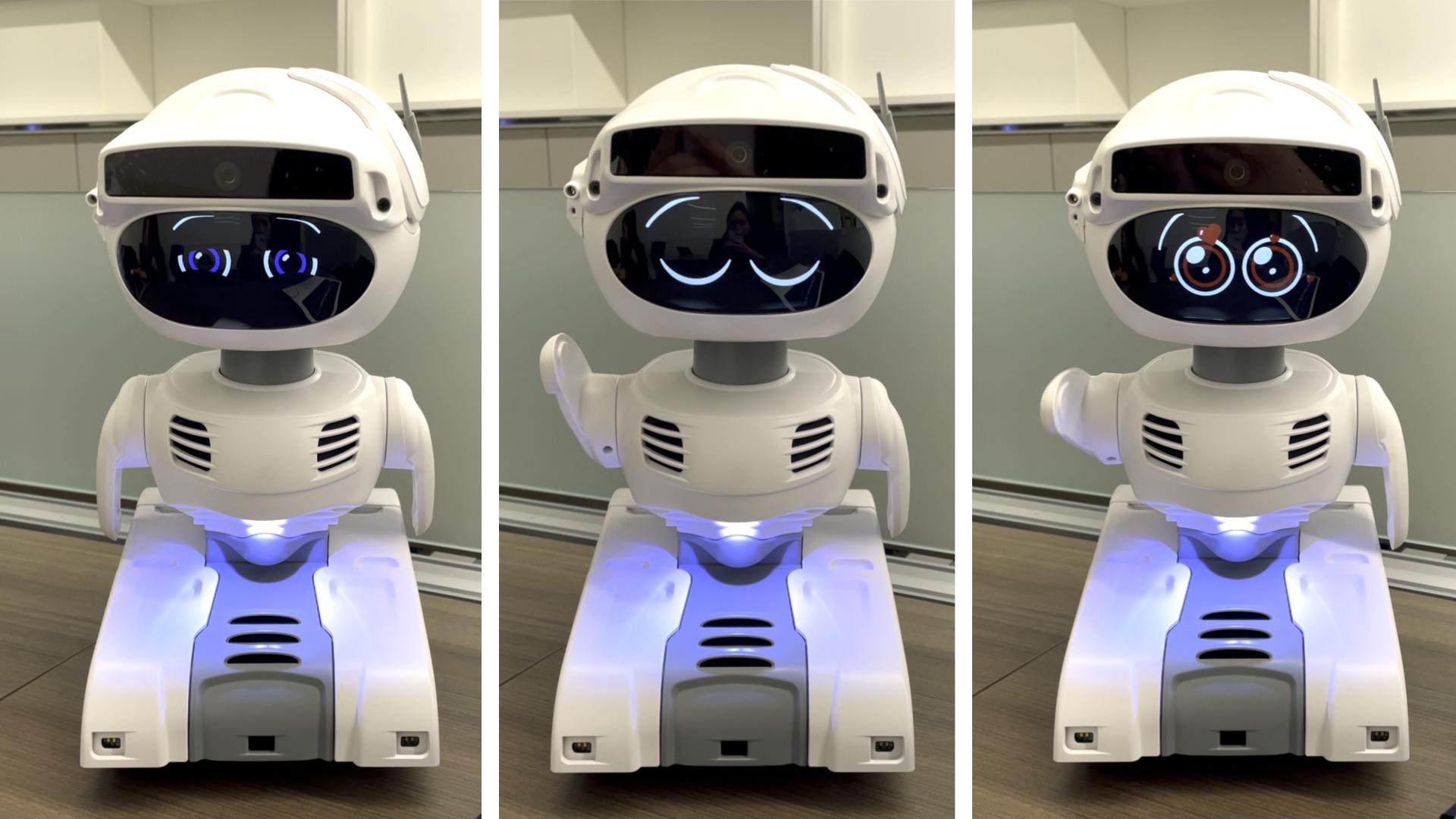
Implementing LLM-Integrated Storytelling Robot
Abstract The prevalence of mental health challenges among college students calls for innovative and accessible support systems. Traditional mental health resources are underutilized due to barriers like financial constraints and discomfort in seeking help. To mitigate these issues, recent research has explored robots for mental health interventions, but their empathy-evoking storytelling capabilities remain underdeveloped. In…
-
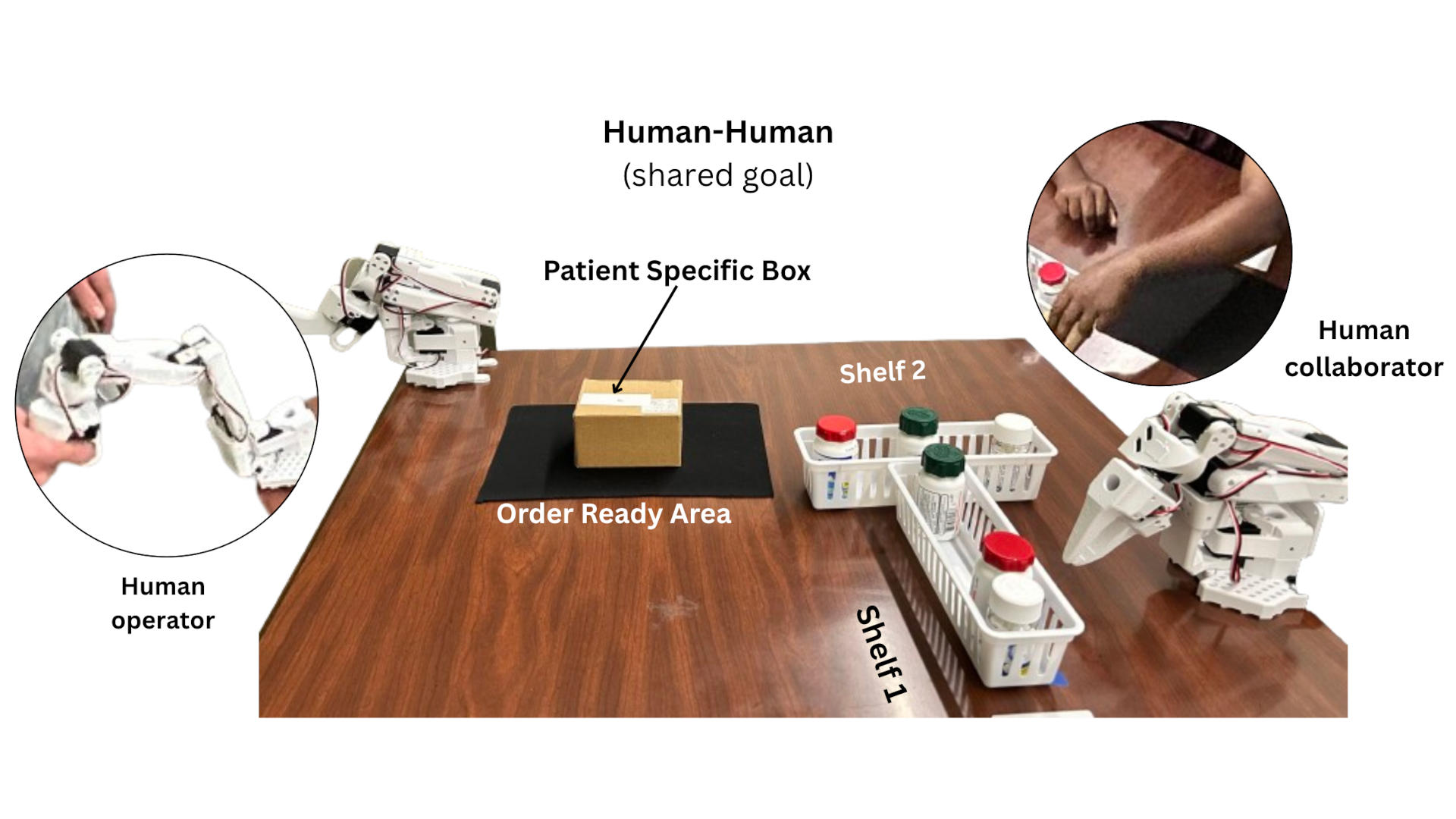
Towards Embodied Agent Intent Explanation in Human-Robot Collaboration: ACT Error Analysis and Solution Conceptualization
Abstract Collaborative robots must not only perform competently but also communicate their intents transparently to ensure safety and efficiency in shared task environments. However, state-of-the-art robot policies such as Action Chunking Transformer (ACT) models are opaque, which may make it difficult for human partners to interpret or predict their actions and intent to facilitate task…
-

Introduction to the Special Issue on Artificial Intelligence for Human-Robot Interaction (AI-HRI)
1 Introduction This special issue of the Transactions on Human-Robot Interaction highlights, documents, and explores the interface between artificial intelligence (AI) and human-robot interaction (HRI). The application of Artificial Intelligence to Human-Robot Interaction domains has proven to be a powerfully effective mechanism for achieving robust, interactive, and autonomous systems with applications ranging from personalized tutors…
-

Causal-HRI: Causal Learning for Human-Robot Interaction
Abstract Real-world Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) requires robots to adeptly perceive and understand the dynamic human-centred environments in which they operate. Recent decades have seen remarkable advancements that have endowed robots with exceptional perception capabilities. The first workshop on “Causal-HRI: Causal Learning for Human-Robot Interaction” aims to bring together research perspectives from Causal Discovery and Inference and Causal Learning, in…
-
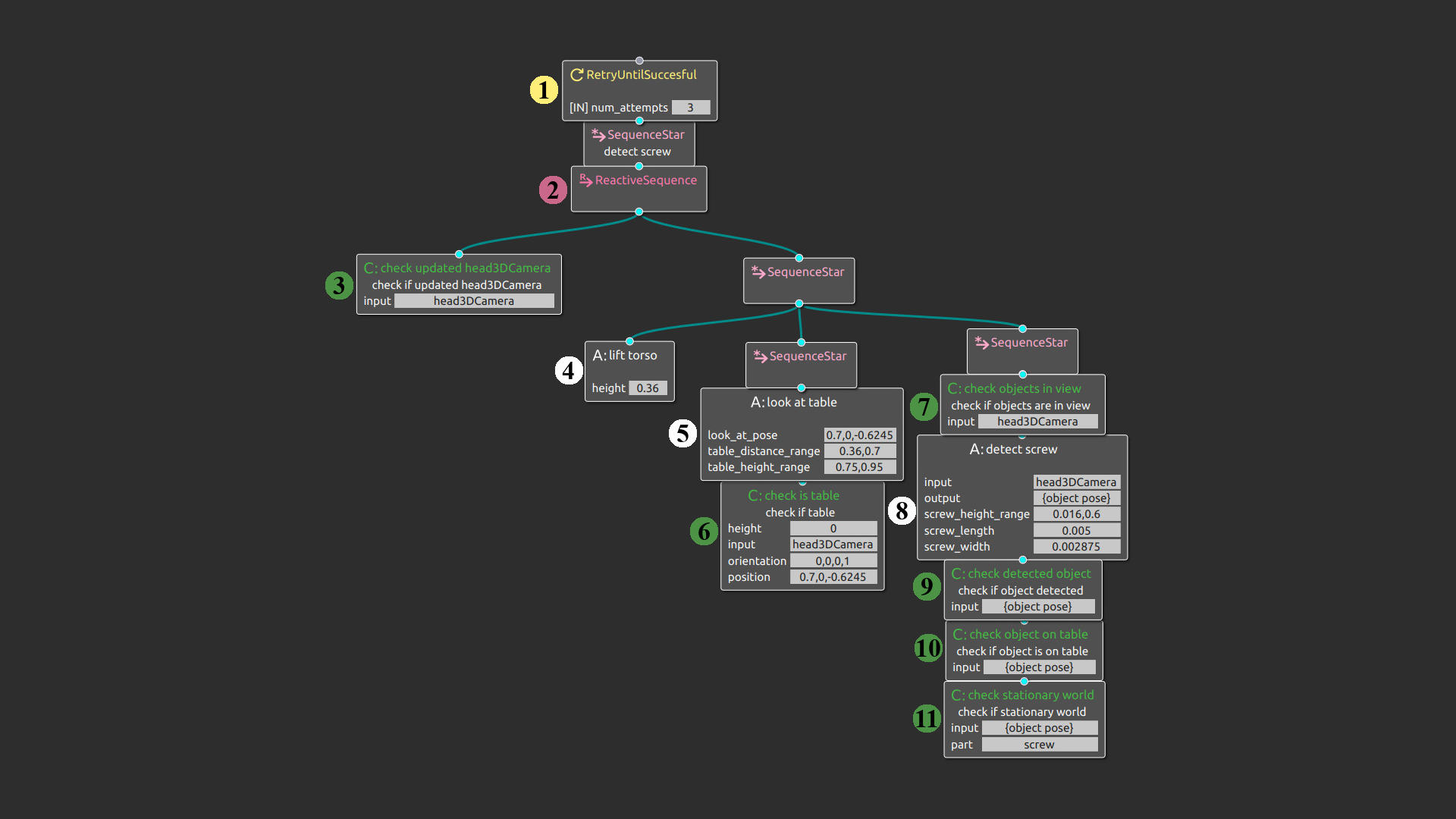
Reactive or Proactive? How Robots Should Explain Failures
Abstract As robots tackle increasingly complex tasks, the need for explanations becomes essential for gaining trust and acceptance. Explainable robotic systems should not only elucidate failures when they occur but also predict and preemptively explain potential issues. This paper compares explanations from Reactive Systems, which detect and explain failures after they occur, to Proactive Systems,…
-

The Importance of Memory for Language-Capable Robots
-

Exploring the Naturalness of Cognitive Status Informed Referring Form Selection Models
-

Evaluating Cognitive Status-Informed Referring Form Selection for Human-Robot Interactions
-
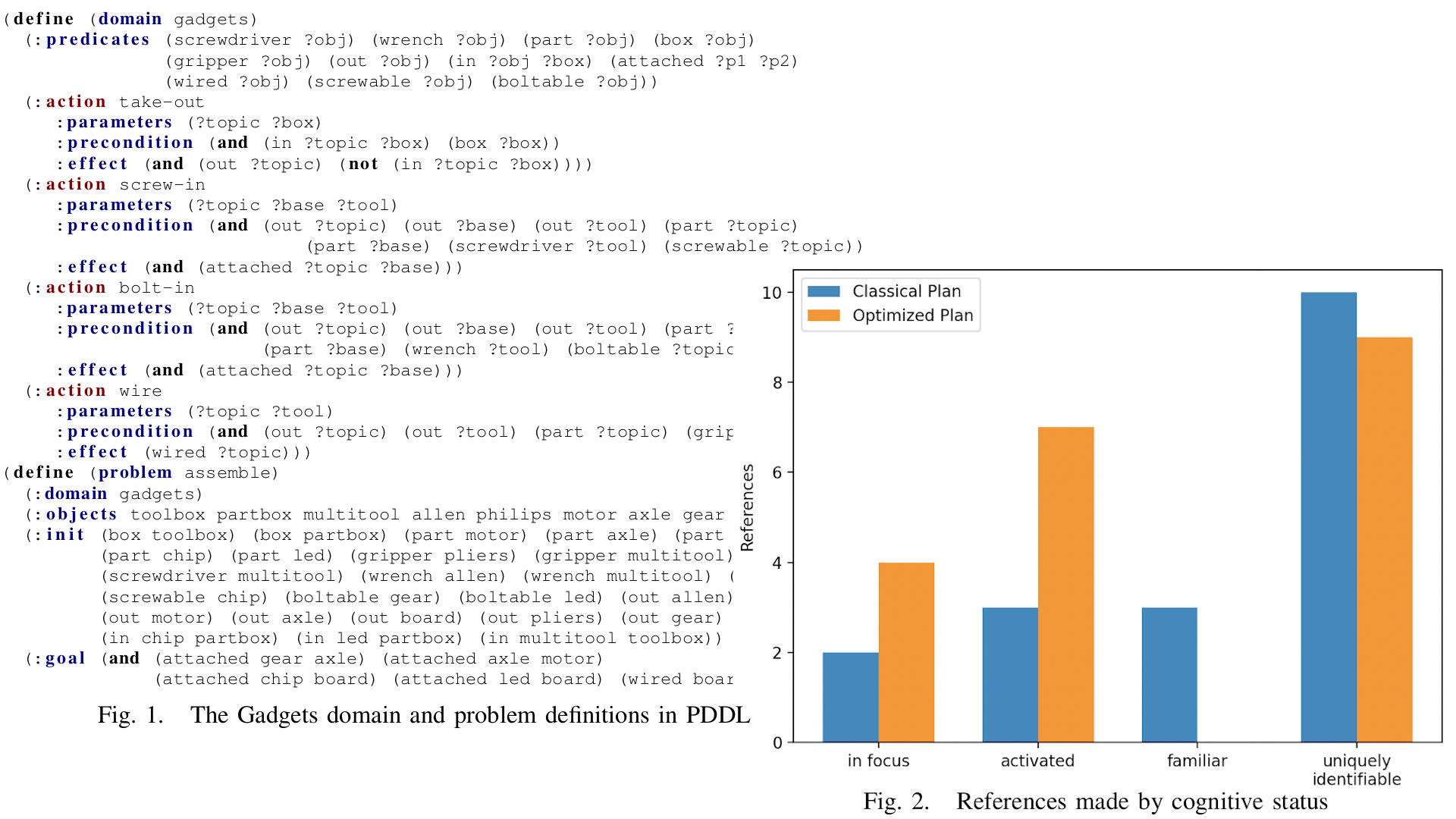
Givenness Hierarchy Informed Optimal Document Planning for Situated Human-Robot Interaction
-
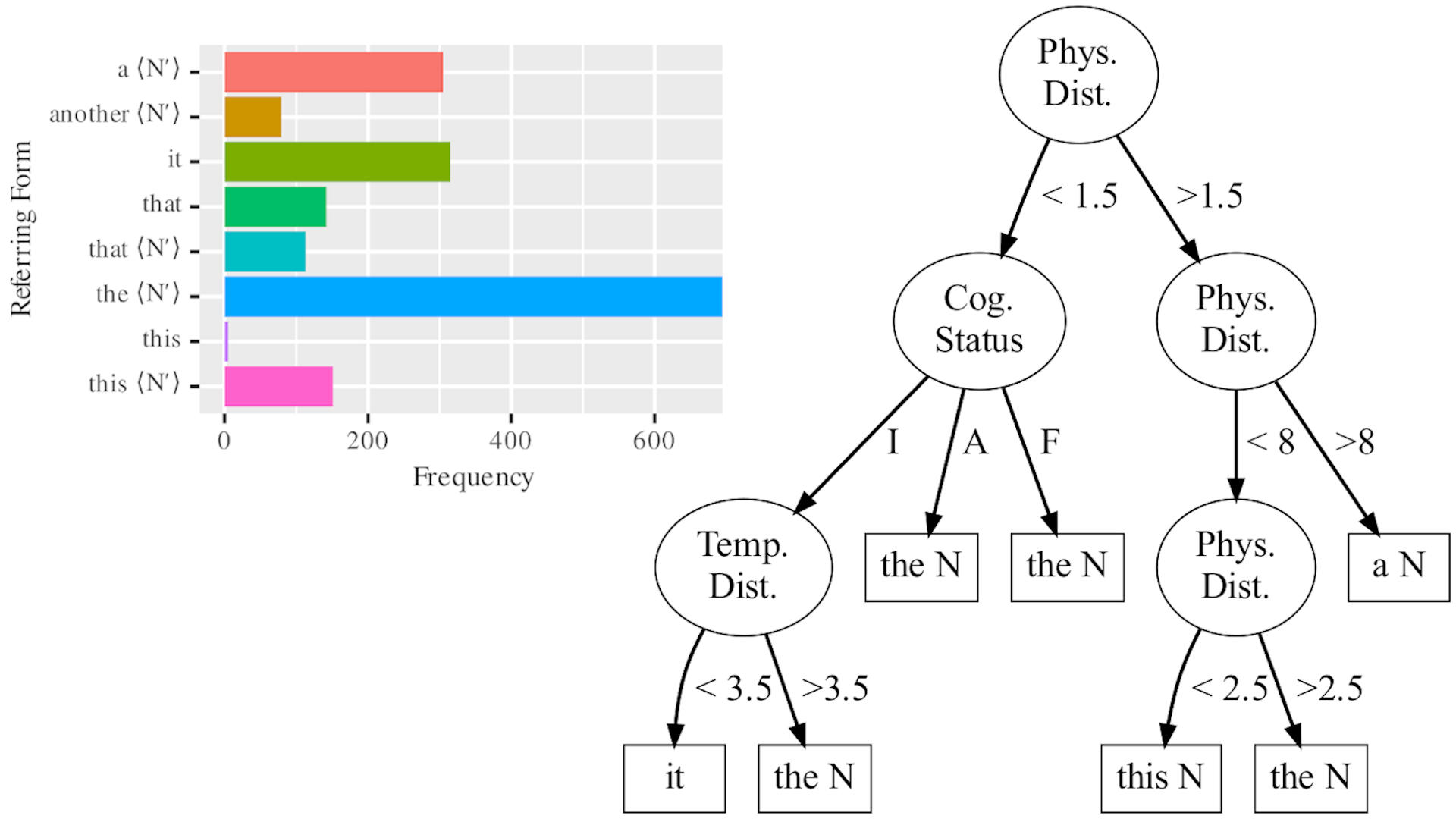
Evaluating Referring Form Selection Models in Partially-Known Environments
-

A Task Design for Studying Referring Behaviors for Linguistic HRI